ICS 212 Final C project
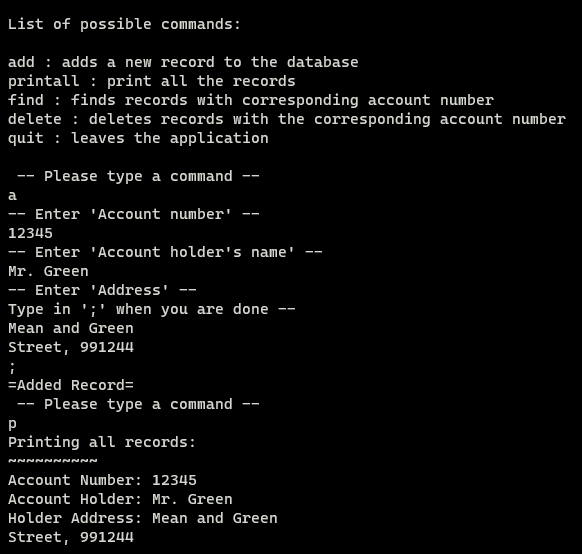
Overview
The final coding assignment in ICS 212, Spring 2023. This project primarily helped me learn how to read and write data into a txt file.
Using a linked list to store account information such as their account number, name and address, allowing for a user to interact and add new entries or remove entries in the database.
When the user is done, the data is saved into a txt file, which will be read upon the next startup of the program.
Difficulties
Saving Data
Writing data to a file
The purpose of the writefile function is to iterate through the linkedlist database, read each record object and save that data into a txt file.
void writefile(struct record* database, char filename[])
{
struct record* curr_Record = database;
FILE *file = fopen( filename, "w" );
while (curr_Record != NULL)
{
fprintf ( file, "%d\n%s%s;\n", curr_Record->accountno, curr_Record->name, curr_Record->address);
curr_Record = curr_Record->next;
}
fclose(file);
return;
}
Memory leak prevention
Accomplished by iterating through the linkedlist, using the free function to release space reserved by the malloc function, before removing their pointers.
void cleanup(struct record** database)
{
struct record* curr;
curr = *database;
while ( curr != NULL )
{
struct record * temp;
temp = curr->next;
curr->next = NULL;
free (curr);
curr = temp;
}
return;
}
Adding data to the linkedlist “database” from a txt file
This readfile function was the main source of difficulty. The reason being the open-ended nature on how to save our data into a txt file. I decided to put each value for each record on their own line. But that causes a problem for an account holder’s address, which allows for multiple line addresses.
void readfile(struct record** database, char filename[])
{
FILE *file;
file = fopen( filename, "r" );
if ( file != NULL )
{
int anum;
while ( EOF != fscanf ( file, "%d", &anum ))
{
char c = '\0';
char aname[30] = "";
char aaddress[50] = "";
fgetc (file);
fgets ( aname, 30, file );
while ( c != ';' )
{
c = fgetc(file);
if ( c != ';')
{
strncat( aaddress, &c, 1 );
}
}
c = fgetc(file);
addRecord ( database, anum, aname, aaddress );
if ( debugMode == 1 )
{
printf( "readfile added a record\n" );
}
}
fclose(file);
}
return;
}
}
Function to create a linked node
All the data collected by readfile is used to create the records in the linkedlist database using this addRecord function.
void addRecord(struct record** database, int actnum, char name[], char address[])
{
struct record* new_Record;
struct record* prev_Record;
struct record* curr_Record;
int done;
if ( debugMode == 1 )
{
printf( "D: addRecord has been called with database** %p, account number %d,\n", database, actnum );
printf( "the name: %s\n", name );
printf( "the address: %s\n", address );
}
new_Record = (struct record*) malloc( sizeof(struct record) );
done = -1;
new_Record->accountno = actnum;
strncpy( new_Record->name, name, 30 );
strncpy( new_Record->address, address, 50 );
if ( *database == NULL )
{
new_Record->next = NULL;
*database = new_Record;
}
else if ( actnum < (*database)->accountno )
{
new_Record->next = *database;
*database = new_Record;
}
else if (actnum == (*database)->accountno)
{
new_Record->next = NULL;
(*database)->next = new_Record;
}
else
{
prev_Record = *database;
curr_Record = (*database)->next;
while ( done == -1 )
{
if ( curr_Record == NULL )
{
new_Record->next = NULL;
prev_Record->next = new_Record;
done = 0;
}
else if ( curr_Record->accountno < actnum )
{
prev_Record = curr_Record;
curr_Record = curr_Record->next;
}
else
{
new_Record->next = prev_Record->next;
prev_Record->next = new_Record;
done = 0;
}
}
}
if ( debugMode == 1 )
{
printf( "\nD: addRecord finished\n" );
}
}
Final Thoughts
What I learned from this project was that I had quite the hard time with pointers. It took me a long time to understand the uses between pointers and dereferences (since they both are signaled with an asterisk).